Fibroids
What are Fibroids? GlobalNews
50-80% of women have fibroids.
Small fibroids (incidental tiny ones) usually do not need any treatment.
If fibroids need to be treated, they can be treated based on symptoms.
Options can treat pain (anti-inflammatories) or bleeding (hormonal or non-hormonal pill, patch, ring, injection, IUD)
or size with the following specifics:
1) Injections with add-back hormone or daily oral medicine (non-affiliated pharma sites) to block the hormones that feed the fibroid
2) Uterine Artery Embolization UHN Interventional Radiology blocks the blood supply that feed the fibroid
3) surgery removes the fibroid
with a telescope through vagina into uterus (hysteroscopy myomectomy) when small fibroid is in the cavity
abdominal surgery (keyhole laparoscopy or laparotomy myomectomy depending on size) if fibroid is in the outer wall
by removal of the uterus if multiple, large, completed childbearing (hysterectomy); leaving your ovaries if not yet menopausal-age
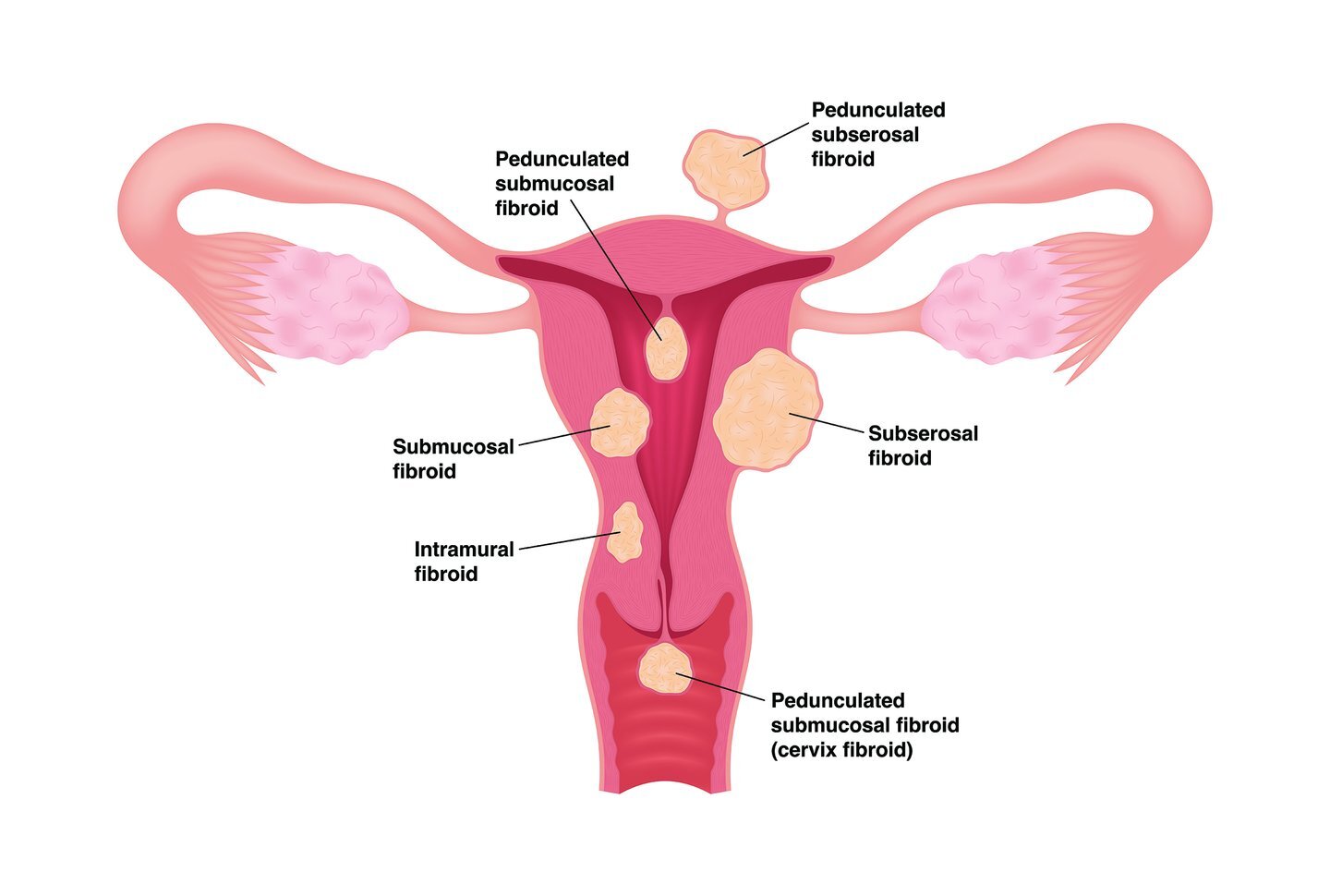
There are 3 main types of uterus fibroids: in the cavity (submucosal), within the wall (intramural), outer wall (subserosal). Pedunculated means hanging by a stalk. Prolapsed means coming out of the uterine cervix. Symptoms depend on where they are located and size. Many people have no symptoms and thus do not need any treatment, as they are more than 99% benign.
Let your doctor know your symptoms and get to know your fibroids.
HOW MANY?
HOW BIG?
WHERE are they located (inside or outside the uterus cavity)?
Is TREATMENT needed (this depends on your fertility plans, any symptoms of bleeding, pain, pressure)?